Regenerative Medicine, 3D Printing & The Future of Orthopaedics
As modern orthopaedics continues to make great strides forward in testing, treatments, and technology, some of the most revolutionary advances are made in the fields of regenerative medicine and 3D printing. Both technologies are helping patients reach better outcomes more quickly and lead more comfortable lives.
What is regenerative medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a new, yet booming field that uses stem cells as the building blocks to promote healing, repairs, and even regrowth in soft tissues and other organs. While some parts of the body already possess the ability to self-heal, regenerative medicine can encourage that same healing power in cells that were once thought to be terminally differentiated, or no longer able to divide. Such cells exist in the heart, lungs, and nerves.
Through a process called differentiation, stem cells can grow into any other type of cell in the body. They can then be used to stimulate damaged organs and tissues to heal themselves. It’s a complex process that involves many biological, biochemical, and biomechanical factors interacting at specific points in time.
For the best chance of success, surgeons often create a blend of stem cells or growth factors obtained from amniotic or umbilical cord tissue, or even the patient themselves, in hopes that it will stimulate healing.
Regenerative medicine has shown promise for treating soft tissues such as tendons and cartilage and their related conditions. And in the future, researchers imagine a world where they can also cure dementia, diabetes, and a host of other degenerative diseases. However, the maturation of stem-cell therapy will be a long and slow process that requires a lot of research, testing, and investment.
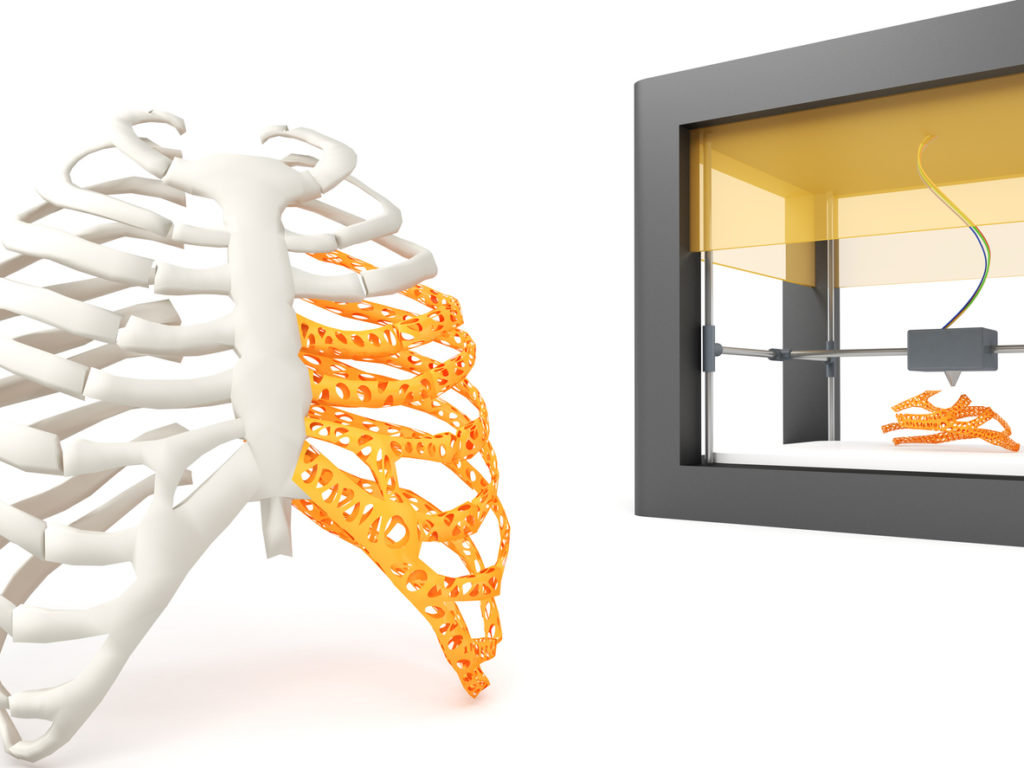
How does 3D printing enhance orthopedics?
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, is helping patients receive truly custom medical implants instead of working with a “one-size-fits-all” solution for all body types, sizes, and situations. Devices including joint-replacement implants—especially smaller joints like fingers and toes—and spinal cages can be created within a range of sizes, and others can be tailored specifically to an individual patient for more complex reconstructions following tumor removal or trauma.
Custom implants and devices are not new, but manufacturing methods have been expensive, time-consuming, and cost-inefficient. But with the rising popularity of 3D printing, they become more affordable for patients and manufacturers. The devices can also be built with complex geometric structures that more naturally mimic the body, detailed surfaces, and porous internal channels that allow for natural bone growth around the implant.
Another important benefit that comes with 3D printing is the opportunity for orthopedic surgeons to use imaging to recreate anatomical models of complex cases. This allows them to both evaluate and even practice a case before a complicated surgery.
The future of orthopaedics holds tremendous promise for personalized treatments that will benefit patients from head to toe, and transform the entire industry. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Daniel Penello today to see if these revolutionary technologies are right for you.
